We provide strategies to land and expand your company in Germany.
- Index
- The Employer of Record (EoR) business model
- What is labor leasing?
-
Global Employer of Record (EoR) Platform operators and their responsibilities
- Case: What does the Cash Flow look like for a global employer of record (EoR) platform operator?
- How to manage the AüG license in the context of a transfer pricing agreement?
- Case: How to manage the relationship with my leased employees when the end customer does not compensate the labor leasing service fee?
- Conclusion
- Summary
- Why Consultinghouse?

Employer of Record (EoR) business models for the German market
In today's globalized and dynamic business landscape, companies often face challenges related to expanding into new markets, managing international workforces, and complying with varying employment laws and regulations. The Employer of Record (EoR) business model has emerged as a strategic solution to address these complexities.
Overview
The emergence of innovative online HR management and Employer of Record (EoR) platforms are transforming the global workforce landscape.
These platforms are not just technology solutions; they represent a fundamental shift in how businesses manage their human resources on a global scale. By streamlining administrative tasks, ensuring compliance with local regulations, and facilitating remote work arrangements, they empower organizations to thrive in the increasingly interconnected world of work.
Online EoR platforms are at the forefront of redefining HR and EoR services, making it easier for businesses to expand their operations globally and enabling talent to work across borders with unprecedented ease. As the world of work continues to evolve, these platforms are at the vanguard, offering agility, efficiency, and a truly borderless approach to HR and EoR management.
Table of content:
- The Employer of Record (EoR) business model
- What is labor leasing?
-
Global Employer of Record (EoR) Platform operators and their responsibilities
- "Case: What does the Cash Flow look like for a global employer of record (EoR) platform operator?
- "How to manage the AüG license in the context of a transfer pricing agreement?
- "Case: How to manage the relationship with my leased employees when the end customer does not compensate the labor leasing service fee?
- "Conclusion
- Summary
- Why Consultinghouse?
The Employer of Record (EoR) business model
INTRODUCTION:
In today's globalized and dynamic business landscape, companies often face challenges related to expanding into new markets, managing international workforces, and complying with varying employment laws and regulations. The Employer of Record (EoR) business model has emerged as a strategic solution to address these complexities. This comprehensive overview will provide insights into the EoR model, its benefits, and why your organization should consider partnering with an EoR service provider.

- Understanding the EoR Business Model:
- Key Components of EoR Services:
- Benefits of EoR Services:
- Why Choose your EoR Service Provider:
- INTRODUCTION TO OSS AUTOMATION
I. Understanding the EoR Business Model:
The EoR business model involves a third-party service provider, the Employer of Record, assuming the legal and administrative responsibilities associated with employing workers in a foreign country on behalf of a client company. This model simplifies global workforce management by transferring HR, payroll, compliance, and legal obligations to the employer of record service provider (EoR).
II. Key Components of EoR Services:
- Global Compliance: EoR providers are well-versed in international labor laws, ensuring that your organization remains compliant with local regulations, including tax, employment, and benefits.
- Payroll Management: EoRs handle payroll processing, tax withholding, and currency conversion, ensuring accurate and timely payments to international employees.
- HR Administration: EoRs manage HR tasks such as onboarding, employee records, and benefits administration, streamlining global HR processes.
- Risk Mitigation: EoRs mitigate legal and financial risks by handling termination processes, employment contracts, and dispute resolution.
- Benefits Management: EoRs often offer benefits packages, including health insurance, retirement plans, and more, tailored to meet the specific needs of international employees.
III. Benefits of EoR Services:
- Rapid Global Expansion: EoRs enable businesses to expand into new markets quickly, without the need to establish a legal entity in each country.
- Risk Reduction: EoRs help minimize compliance risks, avoiding costly legal issues and penalties associated with international employment.
- Cost Efficiency: Outsourcing HR and payroll functions to an EoR can be more cost-effective than maintaining in-house international HR departments.
- Talent Attraction: Access to EoR services can make your organization more appealing to international talent, as it offers local benefits and compliance.
- Focus on Core Operations: EoR providers allow your company to concentrate on its core business activities while they manage administrative and legal aspects.
IV. Why Choose [Your Company Name] as Your EoR Service Provider:
- Expertise and Experience: [Your Company Name] brings years of experience in EoR services, with a team of experts well-versed in global employment regulations.
- Customized Solutions: We understand that every business is unique. We provide tailored EoR solutions to meet your specific needs and help you achieve your global expansion goals.
- Global Network: [Your Company Name] has a vast network of international partners and resources, ensuring seamless operations in numerous countries.
- Technology-Driven: We leverage advanced technology and platforms to streamline HR, payroll, and compliance processes, offering transparency and real-time access to your data.
- Client-Centric Approach: Our commitment to client satisfaction means we provide personalized support and are available to address your questions and concerns.
INTRODUCTION TO OSS AUTOMATION
Selling products online has become a popular way of doing business in the modern world. E-commerce platforms like Amazon and Shopify have made it easier for small and large businesses to reach customers globally.
However, selling in Europe comes with its own set of challenges, including registration for VAT and compliance with tax regulations.
This page will provide a step-by-step guide on how to register as an e-commerce seller in Germany and how to manage and prepare sales transaction data from e-commerce marketplaces like Amazon and Shopify to be prepared for European OSS VAT reporting.
CONCLUSION:
The Employer of Record business model has become a pivotal solution for organizations seeking to expand their global footprint while maintaining compliance and efficiency. Partnering with an EoR service provider like [Your Company Name] can be the key to unlocking international opportunities while mitigating risks and focusing on your core business. By choosing the right EoR partner, you can position your organization for global success and a competitive edge in the international marketplace.
Employer of Record services for the German market
Value Proposition: Exploring Opportunities in Germany for Employer of Record (EoR) Service Providers Germany, a thriving economic powerhouse in the heart of Europe, offers a plethora of opportunities for Employer of Record (EoR) service providers looking to expand their business operations. The primary value proposition for EoR providers considering Germany lies in the potential to leverage the German labor leasing (AüG) license, which enables them to hire toptier talent and lease them to foreign companies. Here's why Germany is an attractive market for EoR service providers:
1. Strong Economy and Business Environment:
Germany boasts one of the largest and most stable economies in Europe. Its business-friendly environment, infrastructure, and robust financial system create a solid foundation for business growth and stability.
2. Access to Highly Skilled Talent:
Germany is renowned for its well-educated and highly skilled workforce. By obtaining the AüG license, EoR providers can tap into this talent pool, allowing them to offer top-tier professionals to foreign companies, meeting their diverse staffing needs.
3. Central Location in Europe:
Germany's central location makes it an ideal hub for international operations. It provides easy access to other European markets, making it a strategic choice for EoR providers looking to serve clients across the continent
4. Well-Defined Regulatory Framework:
Germany's labor laws and regulations are clear and stable. The AüG license framework, while comprehensive, provides a predictable and structured pathway for EoR providers to operate within the legal framework
5. High Demand for EoR Services:
Many multinational companies are eager to enter the German market. EoR services are a compelling solution for them to navigate the complex German employment regulations while swiftly establishing their presence in the country.
6. Diverse Industry Sectors:
Germany is a leader in various industry sectors, including manufacturing, technology, finance, and healthcare. EoR providers can cater to a wide range of industries, finding ample opportunities for talent leasing and workforce management
7. Established Infrastructure and Technology:
Germany offers advanced technological infrastructure, enabling EoR providers to efficiently manage HR, payroll, and compliance services. The country's IT and communication systems are highly developed, supporting a seamless EoR business model.
8. High-Quality Healthcare and Benefits:
Germany offers an excellent healthcare system and comprehensive employee benefits. EoR providers can use these advantages to attract talent and offer foreign clients competitive employee packages.
9. Stability and Predictability:
Germany is known for its political and economic stability, creating a low-risk environment for business operations. EoR providers can count on a predictable regulatory landscape, allowing for long-term planning and growth.
10. Potential for Global Expansion:
By establishing a foothold in the German market and obtaining the AüG license, EoR providers can use Germany as a springboard for expanding their EoR services into neighboring European countries, creating further growth opportunities
In conclusion, Germany's strong economy, skilled workforce, well-defined regulations, and central location make it a compelling market for Employer of Record (EoR) service providers. By obtaining the German labor leasing (AüG) license, EoR providers can offer their clients access to top-tier talent in one of Europe's most prosperous and dynamic economies. This value proposition presents a win-win scenario for both EoR providers and the companies seeking to enter the German market.

Cash flow management for Employer of Record service provider
Cash flow management for an Employer of Record (EOR) service provider involves handling various financial aspects related to their services, which include serving as the legal employer of record for client companies' employees. Here's how cash flow management may look for an EOR service provider:
1. Revenue Generation:
EOR service providers earn revenue through service fees charged to client companies. These fees are typically based on a percentage of the total payroll or a flat fee per employee. Cash flow begins with the collection of these fees.
2. Payroll Management:
One of the primary responsibilities of an EOR service provider is to manage payroll for the employees of client companies. This includes disbursing salaries, taxes, and benefits. EORs must ensure that they have the necessary funds to cover payroll expenses, including employee salaries and employer taxes.
3. Client Payments:
EORs receive payments from client companies for their services. Managing the timing and consistency of these payments is crucial for cash flow. EORs may require upfront payments or have specific billing cycles.
4. Operating Expenses:
EOR service providers have various operating expenses, including salaries for their own employees, office rent, technology infrastructure, legal and compliance costs, and other overhead expenses. Managing these expenses is essential for maintaining a healthy cash flow.
5. Tax Withholding and Remittance:
EORs are responsible for withholding and remitting employee taxes, social security contributions, and other statutory payments. These funds must be held in trust and properly managed to ensure compliance.
6. Reserve Funds:
EORs often set aside reserve funds to cover potential contingencies, such as unexpected payroll or compliance issues, legal disputes, or fluctuations in cash flow due to changes in client contracts.
7. Working Capital:
EORs need working capital to ensure they can meet their financial obligations on time. This includes being able to pay employees on schedule, remit taxes to government authorities, and cover operating costs.
8. Financial Forecasting:
EOR service providers engage in financial forecasting and budgeting to anticipate their cash flow needs. This helps in planning for future growth, compliance, and risk management.
9. Compliance and Legal Costs:
EORs must allocate funds to cover compliance-related expenses, such as legal fees, regulatory reporting, and any penalties or fines associated with labor laws and regulations.
10. Growth Investments:
As EOR service providers expand their client base or offer new services, they may need to invest in marketing, technology, and infrastructure. These investments can impact cash flow.
11. Debt and Financing:
Some EORs may choose to leverage debt or seek external financing to support their operations and growth. Managing debt and financing terms is an integral part of cash flow management.
Effective cash flow management is essential for the financial health and sustainability of an EOR service provider. It requires careful planning, monitoring, and adjustment to ensure that the company can meet its financial obligations, grow its business, and remain in compliance with labor and tax regulations.

What is the dependency between employer of record services and payroll services?
Employer of Record (EOR) services and payroll management are closely interconnected because EOR services often include comprehensive payroll management as one of their core functions. Here's the connection between the two:
1. Legal Employment Relationship:
EOR services involve the EOR becoming the legal employer of record for the employees of client companies. This means the EOR is responsible for payroll processing and managing all aspects of the employment relationship, including payroll-related tasks.
2. Payroll Processing:
As the legal employer, the EOR is responsible for payroll functions, such as calculating and disbursing employee salaries, withholding and remitting taxes, managing deductions and benefits, and ensuring compliance with labor laws and tax regulations. EORs handle these payroll responsibilities on behalf of the client companies.
3. Tax Compliance:
EOR services typically include tax compliance, which is a significant component of payroll management. This involves correctly calculating and withholding income taxes, social security contributions, and other payroll-related taxes. The EOR ensures that these taxes are accurately remitted to the relevant tax authorities.
4. Benefits Administration:
Many EORs also manage employee benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, and other perks. This is often intertwined with payroll management as benefits are typically funded through payroll deductions.
5. Legal and Regulatory Compliance:
EORs must ensure that all payroll-related activities comply with labor laws and regulations. This includes adhering to minimum wage laws, overtime regulations, and various labor standards. They also manage compliance with tax laws and regulations.
6. Payroll Reporting:
EORs provide clients with payroll reports and statements, which detail payroll expenses, tax withholdings, and other financial aspects related to employee compensation.
7. Employee Record Keeping:
EORs maintain employee records, including payroll records, tax documents, and other important HR-related information.
8. Time and Attendance Tracking:
Some EORs offer time and attendance tracking services, which can be integrated into the payroll process to ensure accurate wage calculations.
9. Employment Documentation:
EORs handle employment documentation such as employment contracts, offer letters, and termination letters, which can directly impact payroll processing.
By providing comprehensive payroll management, EOR services relieve client companies of many administrative and compliance burdens associated with employing workers. This allows client companies to focus on their core business activities while ensuring that their employees are paid accurately and on time. The EOR assumes the legal and financial responsibilities of being the employer, making payroll management a central component of their service offering.

Requirements for Employer of Record (EoR) provider to operate in Germany
To become an Employer of Record (EoR) service provider and hire talent in Germany to lease them to foreign companies based on a German labor leasing (AüG) license, you need to meet specific legal and regulatory requirements. The AüG license (Arbeitnehmerüberlassungsgesetz) is designed to regulate and govern temporary employment in Germany. Here are the key requirements for EoR service providers:
Legal Entity in Germany:
To obtain an AüG license, you must establish a legal entity in Germany, which can be in the form of a GmbH (limited liability company) or another recognized legal entity structure.
Financial Stability:
EoR service providers need to demonstrate financial stability and reliability, including having sufficient capital to meet your operational and financial obligations.
Insurance Coverage:
As an EoR provider, you must obtain liability insurance that covers any damages or liabilities resulting from your employment relationships with leased employees.
Compliance with Labor Laws:
Ensure compliance with all German labor and employment laws, including minimum wage regulations, working hours, and other employment-related regulations.
Sufficient Infrastructure:
Establish a physical presence and infrastructure in Germany to manage HR, payroll, and compliance services. This includes having the necessary personnel, systems, and processes in place.
Data Privacy Compliance:
Comply with Germany's stringent data privacy regulations, especially the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other data protection laws. Secure data handling and protection is crucial.
Employee Rights Protection:
Ensure that the rights and protections of leased employees are upheld. This includes adhering to Germany's strong employee protection laws and social benefits.
Negotiating Collective Agreements:
Be prepared to negotiate and comply with collective agreements if applicable, especially in sectors where such agreements are common.
Legal Counsel:
Legal expertise is essential. Seek guidance from German labor law experts and consider hiring or consulting with professionals who are well-versed in the complexities of labor and employment law in Germany.
Regular Reporting and Compliance Monitoring:
Be prepared to provide regular reports to German authorities and to undergo compliance monitoring to ensure that you are following labor and employment regulations diligently.
Language Proficiency:
You will need to operate effectively in the German business environment. Proficiency in the German language, both for business communication and understanding legal documents, can be advantageous.
Business Plan and Documentation:
Prepare a comprehensive business plan that outlines your business model, objectives, and operations. Documentation will be required during the application process for the AüG license.
Application Process:
Follow the specific application process outlined by the German Federal Employment Agency (Bundesagentur für Arbeit) to obtain the AüG license. This process may include submitting financial statements, business plans, and other relevant documents.
It's important to note that regulations and requirements may change over time, so it's essential to consult with legal experts and the German authorities responsible for labor leasing to ensure you meet all the current requirements for EoR services in Germany. Complying with these requirements is crucial to establishing a legitimate and successful EoR business in Germany

What is labor leasing?
Labor leasing, also known as temporary employment, labor hire, or staff augmentation, is a business arrangement where a company or organization temporarily "leases" or contracts the services of workers or employees from an external provider, often for a specific project or period. In this arrangement, the external provider, which could be an agency or a staffing company, serves as the legal employer of the workers they supply to client companies. The workers are commonly referred to as "leased employees."
How is labor leasing defined?
Labor leasing, also known as temporary staffing, labor leasing, or temporary employment, is a work arrangement in which a company (the labor leasing agency) provides temporary or contingent workers to client companies for a specified period. These temporary workers, often referred to as "leased employees" or "temps," are typically employed by the labor leasing agency but work at the client company's location, under the client's supervision, and to fulfill the client's specific staffing needs.
What are the included key features of labor leasing?
1. Employer-Employee Relationship:
The labor leasing agency is the legal employer of the temporary workers. They are responsible for matters such as payroll, benefits, and compliance with labor laws.
2. Temporary Assignments:
Labor leasing arrangements are typically for a fixed and temporary duration, which can range from a few days to several months or even longer, depending on the client's needs.
3. Flexibility:
Labor leasing provides flexibility for client companies to scale their workforce up or down based on demand without the long-term commitments associated with permanent hires.
4. Specialized Skills:
Temporary workers may possess specialized skills or expertise that the client company requires for specific projects, seasonal work, or to cover for absent employees.
5. Regulations:
Labor leasing is subject to labor laws and regulations in various countries, and there are often rules in place to ensure the rights and protections of temporary workers.
6. Licensing and Compliance:
In some jurisdictions, labor leasing agencies may be required to obtain licenses or permits to operate legally, and they must comply with specific labor and employment regulations.
Labor leasing is a common practice in industries that experience fluctuations in labor demands, such as manufacturing, construction, healthcare, and clerical work. It allows businesses to access a flexible workforce while managing their staffing needs efficiently.
What are the key characteristics of labor leasing include:

- Legal Employer
- Cost-Efficiency
- Risk Mitigation
Legal Employer
In labor leasing, the external provider is considered the legal employer of the leased workers. This means they are responsible for HR functions such as payroll, taxes, benefits, and compliance with employment laws.
Temporary Arrangement: Labor leasing arrangements are typically temporary, lasting for a specific project, seasonal demand, or a predetermined period. This flexibility allows client companies to adjust their workforce as needed.
Specialized Skills: Leased employees are often used to provide specialized skills or fill gaps in a client's workforce. They may work in various roles, from administrative positions to highly specialized technical roles.
Cost-Efficiency
Labor leasing can be cost-effective for client companies, as they avoid many of the administrative and legal responsibilities associated with traditional employment. This includes avoiding the need to set up a legal entity for these workers.
Compliance and Legal Framework: In many countries, labor leasing is subject to specific legal regulations and licensing requirements to protect the rights and working conditions of leased employees.
Risk Mitigation
Labor leasing arrangements can help mitigate legal and financial risks for client companies. The provider takes on the legal responsibilities and liabilities of being the employer, reducing the client's exposure to potential employment-related legal issues.
It's important to note that the exact regulations and terminology surrounding labor leasing can vary from one country to another. Some countries may have specific laws that govern temporary employment, and in some cases, they may require providers to obtain licenses or permits to operate as labor leasing companies. Consequently, companies that engage in labor leasing need to be aware of and compliant with the legal and regulatory requirements in their respective jurisdictions.
How important is German labor leasing for employers of record (EoR) service providers to hire talent in Germany in order to lease the talent back to an external company
The German labor leasing license, known as the AüG license (Arbeitnehmerüberlassungsgesetz), is of paramount importance for Employer of Record (EoR) service providers that intend to hire talent in Germany and lease this talent to foreign companies. This license is crucial for several reasons:
- Legal Compliance: The AüG license is a legal requirement in Germany for any organization that engages in labor leasing. It ensures that EoR providers comply with the labor laws and regulations governing temporary employment in the country. Operating without this license can result in severe legal consequences, including fines and legal disputes.
- Employee Rights Protection: The AüG license is designed to safeguard the rights and protections of leased employees. It outlines the terms and conditions under which these employees are employed and specifies the responsibilities of EoR providers regarding their welfare and legal rights.
- Client Assurance: Foreign companies that engage EoR services in Germany are typically looking for a reputable and trustworthy partner. Having the AüG license demonstrates that the EoR provider is authorized to operate within the German legal framework, instilling confidence in clients that the employment relationship is legally sound and secure.
- Liability Mitigation: The AüG license helps define the legal responsibilities and liabilities of the EoR provider in the employment relationship, which can be particularly important in cases of disputes or legal claims. This can limit the exposure of both the EoR provider and the foreign client.
- Risk Management: The license allows the German government to monitor and regulate the labor leasing industry. This helps prevent unethical or illegal practices, ensuring that employees are treated fairly and that the industry operates with integrity.
- Compliance with Labor Regulations: The AüG license mandates compliance with various labor regulations, including minimum wage laws, working hour restrictions, and social benefit provisions. This ensures that leased employees receive the same protections and benefits as any other worker in Germany.
- Avoiding Penalties and Legal Issues: Operating without the AüG license is illegal in Germany, and penalties for noncompliance can be severe. EoR providers that do not possess the necessary license may face fines, legal actions, and reputational damage.
In summary, the AüG license is a legal and regulatory prerequisite for EoR service providers in Germany. It not only ensures compliance with labor laws but also enhances the credibility and trustworthiness of the EoR provider in the eyes of foreign companies and leased employees. Operating without this license is not only risky from a legal perspective but also detrimental to the reputation and reliability of the EoR service provider in the German market. Therefore, obtaining and maintaining the AüG license is of utmost importance for any EoR provider operating in Germany.

What is the labor leasing service agreement and what elements should this agreement include?
A labor leasing service agreement is a legally binding document that outlines the terms and conditions of the labor leasing arrangement between an employer of record (EoR) or staffing agency (the service provider) and a client company (the client). This agreement establishes the responsibilities, expectations, and rights of both parties involved in the labor leasing relationship. Below are the key elements that a labor leasing service agreement should include:
Introduction:
Identify the parties involved, i.e., the service provider (EoR or staffing agency) and the client company.
Scope of Services:
Clearly define the services the service provider will offer. This may include recruitment, HR administration, payroll, benefits management, and compliance with employment laws.
Engagement Terms:
Detail the duration of the agreement, the effective date, and any provisions for renewals, extensions, or termination.
Leased Employee Information
Provide information about the leased employees, such as the number, job roles, qualifications, and any specific requirements or qualifications for the positions.
Rights and Obligations of the Parties:
Outline the roles and responsibilities of both the service provider and the client company, including:
- Compliance with employment laws and regulations.
- Payment of wages, taxes, and other financial responsibilities.
- Handling of HR and employment-related matters, including disputes.
- Management of leased employee benefits, if applicable.
- Insurance and liability coverage for leased employees.
- Access to client premises, equipment, and facilities, if relevant.
Confidentiality and Data Protection:
Specify the handling of confidential information, data protection, and any non-disclosure obligations.
Billing and Payment Terms:
Detail the billing frequency, payment terms, and the structure of fees. This may include the service provider's margin and the costs associated with leased employee salaries, benefits, and administrative services.
Insurance and Liability:
Define the types of insurance coverage held by both parties and how liability for various issues, such as workplace accidents or legal disputes, is allocated.
Termination and Exit Strategy:
Specify the conditions under which the agreement can be terminated, the notice period required, and any exit procedures, including the transition of leased employees.
Dispute Resolution:
Outline the process for resolving disputes between the service provider and the client. This may include mediation or arbitration procedures.
Indemnification:
Clarify the circumstances under which each party may be indemnified in case of legal claims or disputes.
Governing Law:
Specify the jurisdiction whose laws will govern the agreement.
Amendments and Modifications:
Define the process for making changes to the agreement, such as through written amendments.
Force Majeure:
Include provisions for how unexpected and uncontrollable events, like natural disasters or labor strikes, will be handled.
Entire Agreement:
State that the agreement represents the entire understanding between the parties and supersedes any prior agreements or understandings.
Signatures:
Include spaces for authorized representatives of both the service provider and the client to sign and date the agreement.
A well-drafted labor leasing service agreement should be comprehensive, clear, and fair to both parties. Legal counsel with expertise in labor leasing and employment law is often involved in drafting and reviewing such agreements to ensure they meet the specific legal and regulatory requirements of the jurisdiction and industry involved.

What is the significance of the 18-month rule in German labor leasing law, and how does it impact the ability to lease employees to different companies?
In Germany, there is a regulation related to labor leasing, which limits the duration a worker can be leased to another company. According to this regulation:
Maximum Lease Duration:
A worker can be leased to another company for a maximum period of 18 months. This means that a company with a labor leasing license can provide its employees to another business for up to 18 months.
Post-Lease Restriction: After the 18-month period is over, there is a restriction in place. The employee who has been leased cannot continue working for the same customer (the company that hired them through labor leasing) for a period of 3 months and 1 day. This essentially means that the employee must have a break of at least 3 months and 1 day before they can be leased to the same customer again.
This regulation is designed to prevent long-term labor leasing arrangements and ensure that workers have periods of rest or change between assignments to the same customer.
It's important for businesses and employees to be aware of and comply with these rules to avoid potential legal issues and to ensure fair working conditions for the leased workers. If you have any questions or concerns about labor leasing in Germany, it's advisable to consult with a legal expert or authorities who specialize in labor and employment law for the most up-to-date and accurate information.
Frequently asked questions
| Questions | Answers |
|
Would it be possible to lease the very same employee to a different company after the 18 months have expired? |
Yes, it is generally possible to lease the same employee to a different company after the initial 18-month period has expired. The restriction in German labor leasing law typically applies to the same customer, meaning the company that initially hired the worker through labor leasing. |
|
What if the same employee is hired by another labor leasing service provider and is leased to the very same company as before? Will the 18-month rule also apply? |
If the same employee is hired by another labor leasing service provider and is leased to the same company where they previously worked, the 18-month rule is likely to still apply. The rule typically pertains to the specific employee's time at a particular customer, regardless of which labor leasing service provider facilitates the arrangement. |

Global Employer of Record (EoR) Platform operators and their responsibilities
- Due to the war for talent, EoR Platforms are on the rise
- On the way to gaining market share, modern EoR Platform are scaling quickly across markets
- While developing their business, often local laws are compromised and stretched over speed
- Especially in Europe, every country has its own rules and regulations
- Especially in Germany EoR service providers and digital platforms need to respect the German AüG law

Case: What does the Cash Flow look like for a global employer of record (EoR) platform operator?
| Intendend | Risks |
|
The EoR provider in Germany leases its employees in Germany to external companies |
A German labor leasing license needs to be hold and maintained by the German legal entity of the global employer of service provider. |
|
The service fee (salary costs + admin & administration e.g. payroll) is paid by the monther company in Singapore based on an internal Mutual Service Agreement (MSA) |
A labor leasing service agreement needs to be closed with the end customer and the German legal entity directly. |
|
The service fee (salary costs + admin & administration e.g. payroll) is paid by intl. end customers to the mother company in Singapore. |
Based on the labor leasing service agreement between the end customer and the German legal entity the service fees may be collected directly by the German legal entity. |
|
The mother company in Singapore transfers the costs +5% to the German legal entity against a monthly IC invoice |
As the employees are leased to external companies and the external companies need to finanially compensate the German legal entity directly for the labor leasing services, the employee cost may be excluded from the transfer pricing agreement (TPA) which the German legal entity has in place with its mother company based in Singapore. |
Typical implications of global Employer of Record (EoR) online platform provider
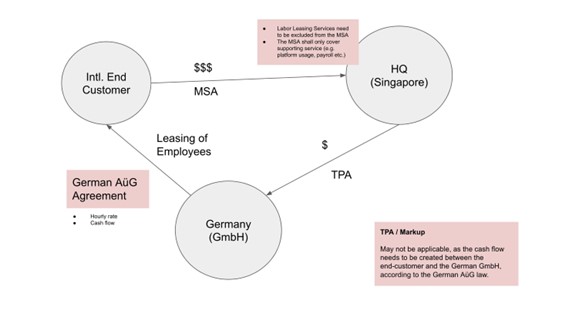
Global Employer of Record (EoR) online platform provider may shift their operation model to stay compliant from a German labor leasing perspective
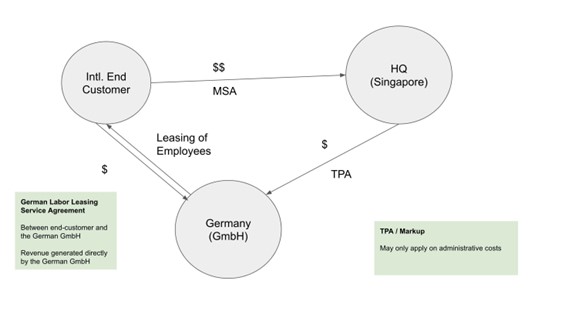

How to manage the AüG license in the context of a transfer pricing agreement?
| Questions | Answer | Which law |
|
Is it possible to collect the budget for Labor Leasing Services from end-clients via the HQ inSingapor, if the Labor Leasing service agreement has been closed/signed between the German company and the end-customer? |
No. |
|
|
If the Labor Leasing agreement is closed between the end customer and the German legal entity, does the German legal entity have to collect the budget from end clients? |
Based on the Labor Leasing Agreement the hourly rate is defined, and therefore the hours for each employee needs to be tracked and invoiced to the end-customer by the German legal entity. |
German AüG law |
|
What is the hourly rate? |
The hourly rate needs to be negotiated / calculated to cover all expenses |
German AüG law |
|
Is it possible to exclude the employee cost from the Markup (TAP)? |
This question might not be relevant, as under German AüG law, the revenue for labor leasing services needs to be generated directly from the end-customer based on a German AüG Labor Leasing Agreement |
German AüG law |

Case: How to manage the relationship with my leased employees when the end customer does not compensate the labor leasing service fee?
Problem
- EoR that the demarcation of roles is not clear within the complicated organizations of EoR providers
- An employee is always exclusively assigned to one customer → Therefore termination is the only option
- The internal processes of global EoR providers are very complex as basically different teams are involved and these teams are not familiar enough with local laws
Implications with regard to internal processes & procedures
- Operational Finance Team
- notices that the end customer does not pay
- Informs the operational payroll team
- Operational payroll team
- informs the internal legal team
- The operational legal team
- fills in a template/process
- Has this template been signed by the managing director
- provides the termination letter back to the operation payroll team
- The operational payroll team
- sends the termination letter to the employee
Key criteria
- The EoR provider must be in possession of an AüG license.
- It should be known at the beginning, how long the employee can be used with a customer
|
Business end customer Relationship |
||
|
Business case |
Contract |
Requirements for the AüG contract |
|
The end customer does not pay his invoice to the EoR provider |
Depends on the end customer's agreement |
The customer is contractually obligated to pay the agreed hourly rate |
|
Own Employees Relationship |
||
|
What effect does this have on the employee hired |
Requirements for the AüG employment contract |
Periods of notice in the AüG employment contract (In case of application of a collective agreement) |
|
EoR can simply terminate the employee if the end customer does not pay. In compliance with the notice period salary must be paid until the end of the notice period |
Indefinite: When there are multiple employment opportunities for the employee Fixed-term: If the employee is only provided for one end customer. In this case, the employment contract should be issued for a maximum of 18 months. |
In the first 4 weeks 2 days from the 5th week until the end of the 2nd month: 1 week from the 3rd-6th month: 2 weeks from the 7th month onwards the statutory notice periods apply: 4 weeks to the 15th or to the end of the month |

Conclusion
- The relationship with the end customer should not be mixed with the employment relationship with the employee.
- If an end customer does not pay for frequent labor leasing services, then this must be clarified on the business side with the end customer.
- Hence, the employee is employed based on a German work contract and therefore the relationship with the employee needs to be taken care of independently
- In the case of the employee situation, the employment contract must be taken into account, especially the notice periods stipulated in the collective agreement.
A summary of concrete focus areas that need to be taken care of by EoR service providers operating in Germany
- Labor Leasing (AüG) License
- Obtaining a German labor leasing (AüG) License
- Planning for the renewal of the German Labor Leasing (AüG License) in 12 months
- Introducing timesheets to track hours and availability for each leased employee
- Daily Execution (AüG)
- Introducing and maintaining Labor Leasing (AüG) compliant German work contract
- Introducing processes to have German-AüG-compliant work contracts signed in wet-ink (within 2 weeks)
- Introducing solutions to address the 18-month limitation (AüG employees can only be leased for up to 18 months without a break)
- Operating model “ Global Platform business”
- Introduce a Labor Leasing (AüG) Service agreement between the EoR service provider in Germany and the end customer
- The EoR service provider in Germany needs to issue service invoices directly to the end customer
- Transfer Pricing Agreement
- Separate inter-company invoices for EoR services from management services
- Harmonize markup for EoR services with the rates defined in the Laboar Leasing (AüG) service agreements between the EoR service provider in Germany and the end customer
The EoR service provider operating in Germany should be prepared for the possibility of an audit by German authorities within the first 3 years of starting its operations in Germany. To avoid substantial penalties, it is important to align our current operating model with their expectations and requirements. In parallel, the EoR service provider that is operating in Germany must take all necessary steps and measurements to ensure that the Labor Leasing License is renewed within the next 12 months.
Why Consultinghouse?
Are you an Employer of Record (EoR) company looking to establish a solid foothold in the thriving German market? Look no further!
Consultinghouse is your seasoned partner with a track record of excellence in helping EoR businesses navigate the intricacies of the German business landscape.
Our team of management consultants, HR specialists as well and payroll professionals will deliver added value to EoR service providers when scaling their business in a strong German market.
🌐 Expertise in Establishing Operating Models
Our journey is paved with a wealth of experience in supporting Employers of Record companies, like yours, to successfully establish and grow their operating model in Germany. We understand that setting up shop in a new market can be challenging, but with Consultinghouse by your side, you can confidently enter the German business arena, leveraging our knowledge and expertise.
💼 Monthly Payroll Accounting:
As a vital component of our comprehensive services, we specialize in precise and reliable monthly payroll accounting. Whether it's calculating employee salaries, managing tax withholdings, or navigating the intricacies of German payroll regulations, we've got you covered. Our commitment is to ensure that your employees are paid accurately and on time, so you can focus on what matters most - growing your business.
🤝 HR Management & Advisory Services:
At Consultinghouse, we pride ourselves on being more than just a service provider. We are your strategic partner, working hand in hand with EoR customers to address their HR management and advisory needs. From onboarding to compliance and beyond, our team is dedicated to supporting your growth and ensuring that your HR practices are in line with German regulations.
📈 Unlock the German Market's Potential:
Germany offers a wealth of opportunities for global businesses, and with our guidance, you can unlock its full potential. Our solutions are tailored to meet your specific needs, helping you operate seamlessly and confidently in this dynamic market.
Don't miss the chance to partner with Consultinghouse, where experience, dedication, and a commitment to your success come together to ensure your EoR business thrives in Germany. Contact us today to explore the possibilities and take your business to the next level.

Disclaimer
This article is for information purposes only. No business decision shall be taken based on the information provided. All legal services are provided by Katerina Koleva, attorney for German labor law
Labor leasing regulations can be complex and may vary, so it's crucial to consult with legal experts or authorities specializing in labor and employment law to ensure compliance with the specific rules and regulations in a given situation.
SEAMLESSLY EXPAND YOUR BUSINESS TO GERMANY
TO LEARN MORE ABOUT HOW WE CAN ADD VALUE TO YOUR BUSINESS IN GERMANY, PLEASE DO NOT HESITATE TO CONTACT US TODAY!
Book your advisory call today
We help you to assess the current phase of your business and to build your personal roadmap about how your business can start and grow in Germany.
Market Entry Newsletter
Our newsletter covers the news you need. Subscribe now.











.png?width=512&height=512&name=union%20(4).png)